Overview of Multi-Degree-of-Freedom Modulation Techniques for Dual Active Bridge Converter
Abstract
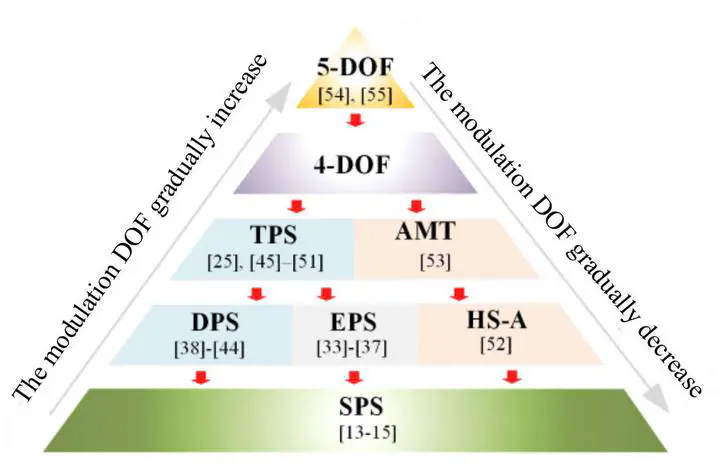
With the increasing popularity of renewable energy and electric terminal equipment, the large-scale application of isolated bidirectional dc–dc converters (IBDCs) is growing. Among these converters, the dual active bridge (DAB) converter, as the core topology of IBDCs, has garnered significant attention due to its bidirectional power transmission capability, simple modularity, and wide soft-switching range. To enhance the efficiency of DAB, various multi-degree-of-freedom (M-DOF) modulation techniques and related solutions have been proposed. However, there is currently a lack of in-depth understanding and thorough comparison of different M-DOF modulation techniques, making it difficult to obtain the optimal solution for different application scenarios. Therefore, based on the latest research and contributions, this article provides an overview of M-DOF, including models, objectives, and algorithms. Furthermore, the existing typical M-DOF modulation techniques are compared through experiments, exploring the differences and advantages among these technologies. Through these analyses, this article offers robust support for the advancement and application of M-DOF modulation techniques in DAB converters.